Approximating 3×2

One Must Imagine Sisyphus Approximating 3+1 (extended)See more

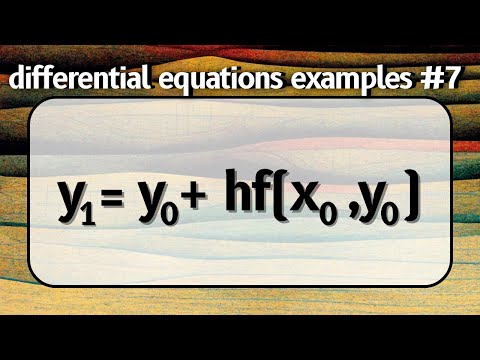
3 Methods of Approximating First-Order Differential Equations -- Differential Equations Examples #7See more
Section 6-2 Video 3- Approximating Areas with Riemann Sums- Part 2- Video 1See more

APPROXIMATION (Target-100) || One Shot-Topic-2 || Must watch!See more

Approximating 3×3See more

Numerical Integration using Simpson's 1/3 Rule: Approximating Definite IntegralsSee more

Approximating 2+2See more

4th Order Runge-Kutta Method for Approximating a Solution to a First Order IVPSee more

1 1 3 Approximating AreaSee more

Day 3, Lecture 2 of Sublinear-Time Algorithms for Approximating Functions of Many VariablesSee more

Find the third degree Taylor polynomial for f(x) = x^(3/2) centered at x = 4. Taylor seriesSee more

Binomial ApproximationSee more

Use series to approximate definite integral x cos(x^3) dx to three decimal places.See more

Use series to approximate definite integral x^2 e^(-x^2) dx to |error| less than 0.0001See more

How to Use the Midpoint Rule to Approximate an AreaSee more

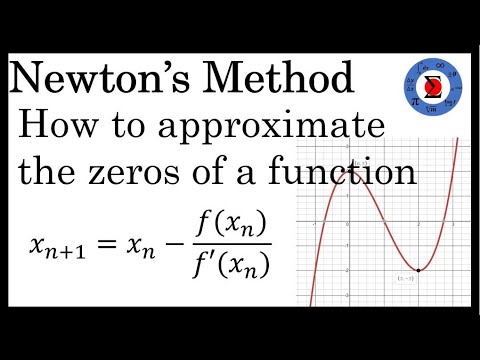
Newtons Method - Approximating a Zero of a FunctionSee more
July 2 Class 13 Fundamentals Of Geodesy : Chapter-3: Approximating The Naural System Of CoordinatesSee more

1 + 1 = 3 Proof | Breaking the rules of mathematicsSee more
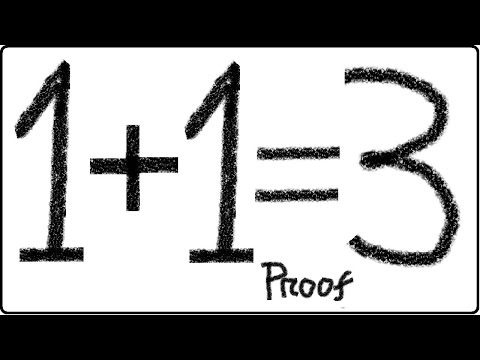
Numerical Differentiation | Forward, Backward and Central Difference | Numerical ComputationSee more
